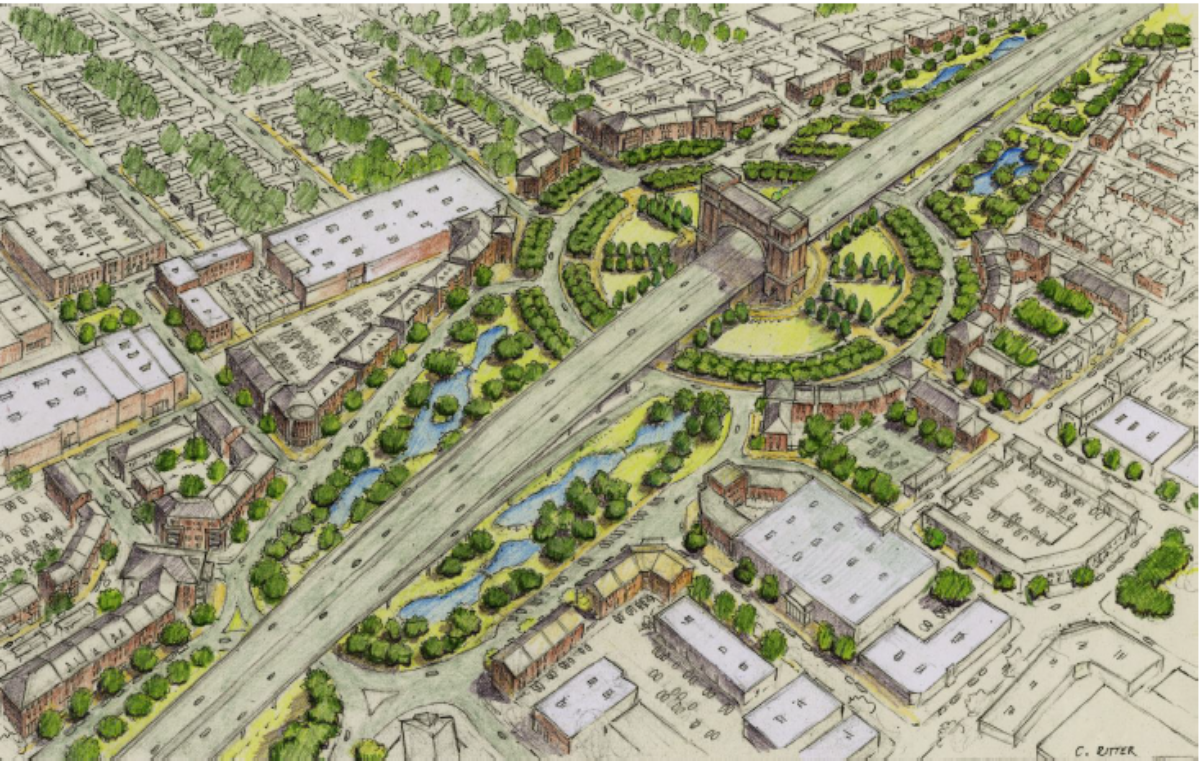
Just as it is becoming more and more clear that an elevated I-49 Connector through Lafayette is the most feasible cost-effective option for building the freeway; it is just as clear that the opposition to this project is as loud as it has been since the concept has been planned.
While most opposition to the Connector is mostly based on sheer NIMBYism of not wanting an elevated structure next to their neighborhood; there are also legitimate concerns about contamination of the Chicot Aquifier, which supplies Lafayette’s drinking water, as well as the costs of constructing the freeway, as opposed to the combination of looping the freeway around Lafayette (most often proposed through the Teche Ridge Bypass alternate through St. Martin Parish, less proposed through the Lafayette Regional Expressway loop to the west around Lafayette’s perimeter). As the process of Conceptual Design and the Supplemental Environmental Impact study proceeds, the opposition to the Connector has become a bit more active in stating their views.
Over at the Sierra Club’s “Y-49” Facebook page, a citizen and long-time opponent of the Connector freeway named Roger Peak just posted a letter “for the record” that he sent to the Lafayette Connector Partners (the group entrusted by LADOTD and FHWA to oversee the design process for the project) during their most recent Open House Public Meeting. The letter, actually written by another opponent of the Connector named Dennis Sullivan, essentializes the main points of opposition to the Connector and support for a combination of a bypass and “improvements” to the Evangeline Thruway via a “boulevard”. The full letter is below:

My goal here is not to disrespect Mr. Peak, Mr. Sullivan, or any other opponent of the Connector freeway or deny them their right as citizens to protest and oppose this project. However, as an proponent of the Connector, I do feel it’s within my reason to challenge some of Mr. Sullivan’s points and statements. I will critique as I follow his letter.
1) Chicot Aquifer Protection
First, the relevant portion of Mr. Sullivan’s letter:

The 2003 Record of Decision for the Connector project stated that there was more than adequate protection for the Chicot Aquifer since the clay layer that protects the permeable area runs nearly 40 to 60 feet thick below ground level. Pilings that would be driven for the elevated structure would go no deeper than 30-35 feet, well before the aquifier surface would be breached; and universally approved best practices and standard procedures would be enabled and executed to ensure that the aquifer is fully protected.
The one main area of concern has always been the site of the former Southern Pacific Railroad distribution yard, where contamination of the soil just below the surface has been found and documented. Opponents of the Connector cite correctly the risk of pilings surrounding the contaminated surface breaching the clay protective layer, threatening the aquifer. LADOTD has responded that the site is eligible for a full remediational cleanup, and that standard practices and procedures will be undertaken to protect the aquifer levels.
LADOTD and the Connector Design Team recently issued a presentation documenting all the issues of protecting the Chicot Aquifer and the means of protections available. The presentation is presented below.
More than likely, this will not ease the concerns of Connector opponents, who are simply locked in to opposing the freeway through Lafayette under any circumstances. However, to say that LADOTD or FHWA is simply not concerned at all about protecting the aquifer is simply not true. Also, invoking the Flint, Michigan water contamination debacle, which was a large scale man-made disaster based on political motives of privatization rather than an isolated incident of a small breach of property, is emotional scaremongering at its worst.
It should also be noted that there is a current standing lawsuit ongoing against Union Pacific Railroad (the current owners of the property of the former Southern Pacific railyard) to have them pay the full costs of any remediation and clean up of that facility. Since remediation and cleanup is a mandated requirement for constructing the Connector freeway, regardless of whomever ultimately pays the bill, using this as a reason for opposing the freeway is a bit deflective reasoning.
2) The Evangeline Thruway and the Connector Freeway: Heartbeats or Heart Stakes??

Here, Mr. Sullivan (and by relay, Mr. Peak) invokes the construction of the original Evangeline Thruway through Lafayette during the 1950’s and the supposed destruction of the neighborhoods it traversed in order to avoid what he believes to be the same mistake with the Connector. Problem is, he entirely misses the point about why the Evangeline Thruway was originally built, and how it has actually affected Lafayette.
Evangeline Thruway was originally designed to be an opening step towards an ultimate freeway facility going north-south (or, more accurately, north-southeast) through Lafayette. The wide median built at Willow Street was done explicitly to accommodate a future interchange; the 250 foot spacing between the one-way couplet (compromised only near Simcoe Street in order to avoid conflicts with the St. Genevieve Catholic Church facility) was designed to originally occupy an elevated freeway, and the accommodating roadways it connects (US 90 and US 167) were also created with full intent of ultimate upgrade to a limited access freeway. Temporary direct access was allowed in the initial stages of construction, but ROW acquisition for both the segments of US 90 south of Lafayette and US 167 north of Lafayette was designed for ultimate freeway upgradability. (US 167 was subsequently upgraded to a freeway to and beyond Opelousas as part of the original I-49 project to Alexandria and Shreveport.)
As for the apparent damage the Thruway has done to the “proud neighborhoods of the railroad’s Black middle class”? That’s a very interesting assertion; especially considering the explosive growth of Lafayette during the 60’s and 70’s due to the petrochemical boom and the development of the main university (first SLI, then USL, now UL(L). The oil glut of the 90’s did do some damage to Lafayette economically, but that was more an overall impact. Was the Thruway responsible for the rise and decline of Northgate Mall or the decision of Walmart to locate their Northside Supercenter there?
Currently, the Evangeline Thruway serves as the main source of access to both downtown (via mostly the Second Street/Third Street couplet, Jefferson Street, and Johnston Street), UL (via Johnston Street and University Avenue) and the Lafayette Regional Airport (via Surrey Street). It also serves as the main artery of access to the rapidly growing suburban enclaves further south, such as Youngsville and Broussard, and ultimately via US 90 south to New Iberia, Jeanerette, Baldwin, Franklin, and Morgan City. Is Mr. Sullivan saying here that things would be better if the Thruway wasn’t constructed to begin with?
In addition, you can make a serious case that the same railroad that apparently brought out the “great Black middle class” also caused the very division of the city of Lafayette as much as the Thruway, especially due to the centralized location of the former rail yard (before it was moved to the western fringes near Walker Road).
In any case, all this also ignores the basic fact that the proposed Connector freeway alignment simply uses most of the Thruway in order to be the least divisive and destructive. Other than a twelve block section of the median of the Evangeline Thruway from the Louisiana & Delta railroad spur crossing to around Simcoe Street, and a segment of the alignment straddling Chestnut Street, there are few if any residential displacements. And, the Elevated concepts under consideration allow for full and open access underneath the mainline structures for both people and vehicles to cross underneath, while deflecting the overwhelming majority of the heaviest traffic onto the mainline structures away from the surface streets. (The Depressed options bring forth their own benefits and risks; that is another story entirely.)
In any case, all this sounds like mere NIMBYism and fear of adjustment and a desire for restoring the mythology of isolated, close-fit neighborhoods where people merely walked 10 minutes to the local store or merely sat on their porches. In reality, Lafayette is not simply a patchwork of Port Barres and Abbevilles with a downtown hub; it’s a moderately-sized city which depends on transportation facilities that simply don’t meet their current demand, let alone the growth of the future.
3) The “Freeways to Boulevards” Fraud That Doesn’t Work

Here, Mr. Sullivan invokes a transportation concept that has become very popular of late for urban planners and car/freeway haters alike: the idea of pushing traffic away from currently elevated through freeway routes by converting them to surface at-grade boulevards for “economic development”. This “freeways to boulevards” concept took off with developers who wanted to tear down and tear up “ugly” elevated freeways that they claimed to obstruct the natural view and destroy inner city neighborhoods. The idea is that traffic wanting to merely pass through these cities are perfectly free to take long-way bypasses around them, but those wanting to go through them should be forced to slow down and traverse stoplights, bike lanes, and other obstructions so that they can stop and discover the beauty of those neighborhoods.
So far, there have been only a few communities that have attempted the “freeways to boulevards” concept, with mixed success. New York City had their Central Expressway downgraded to Central Avenue; and San Francisco after the devastating Loma Prieta earthquake of 1989 took out a double-deck section of Interstate 880 in Oakland, decided to simply rebuild it as a surface boulevard. That hasn’t stopped the New Urbanist faithful from gleefully pushing the concept on other cities. Freeway teardowns and boulevard conversions are currently being proposed in Kansas City (the southern Inner Loop section of I-70); Syracuse (I-81 through downtown), and New Orleans (the I-10 Claiborne Avenue viaduct).
Notice the disclaimer “proposed”, though. None of those proposals have been enacted, and alternatives that either preserve and improve the elevated segments or convert them into depressed/covered freeways with development allowed over them, are also under consideration. The main concern is that these new “boulevards” will not be able to handle the level of traffic that will remain on them, even with the diversion to bypass routes. Of course, that’s considered mostly a benefit for the New Urbanists; the better to force them to either stop in these neighborhoods or switch over to alternative means of transport (walking, bikes, buses, light rail).
It should also be noted that most of the freeway teardowns that are being implemented are isolated segments where alternative routes are being built or improved to meet the adjusted traffic need. In Houston, they are implementing the removal of the Allen Avenue Viaduct segment of Interstate 45 between I-10 and the US 59/Future I-69 stack interchange….but they are rebuilding and realigning I-45 along I-69 north to I-10 and then west on I-10 to maintain proper capacity. In most cases, the freeway segment is simply being dropped down (as in the Boston Central Artery/”Big Dig” project) or shifted along a close new alignment (as with the Dallas “Mixmaster” and “Horseshoe” projects along I-30 and I-45).
The relevance to the Lafayette Connector project, you ask? Well, opponents of this freeway have been pushing since the beginning for construction of an I-49 bypass along the eastern fringe of Lafayette, utilizing the Teche Ridge through St. Martin Parish. (Some have also been promoting a much longer bypass along the southern and western fringes of Lafayette Parish, called the Lafayette Regional Expressway, but the prohibitive costs and distance of that alternative deems it less attractive as a bypass alternative.) To them, Teche Ridge is a more “common sense” alternative that would avoid all the displacements and destruction of the Connector project, and allegedly at half the cost.
Most recently, Connector opponents have taken to proposing a combination proposal: build Teche Ridge as the I-49 South bypass, but also convert the Evangeline Thruway into a “high-speed” yet “neighborhood friendly” boulevard to handle the traffic that would use it. The claim is that Teche Ridge would remove enough traffic from the Thruway that the new “boulevard” would be able to both handle the remaining traffic and promote the appropriate development for the neighborhoods surrounding it.
One look at LADOTD’s current and projected traffic projections for the Evangeline Thruway puts that theory to bust. This is from the Lafayette Connector website, given as part of the third Open House Public Meeting last November.

The above graph shows the current traffic volume (based on 2015 values) on the Evangeline Thruway, listed as Average Daily Traffic (ADT). Notice that the Thruway couplet is listed as carrying 64,000 to 70,000 vehicles per day; which would be straining it for a four-lane freeway, let alone a six-lane arterial/2×3 one-way couplet.

Now we get to the projected ADT for 2040, provided that the Connector freeway is not built. Notice how the ADT values for the Thruway now jump to 86,000 VPD north of Johnston Street, and 95,000 VPD south of there heading towards Pinhook Road and the airport. Yeah…a boulevard will certainly handle that.
But, you say, won’t Teche Ridge divert enough traffic from the Thruway to make a boulevard possible? That’s what all the Connector critics say….but most credible studies show otherwise. In both 1993 with the North-South Corridor Study and in 2003 with the original Connector Final EIS/ROD documents, Lafayette Consolidated Government traffic engineers have done traffic studies on the Thruway to see what percentage of the Thruway traffic is truly bypassing the city rather than accessing places within the city. Their results consistently confirm that only 10 percent of the traffic on the Thruway is traffic bypassing the city; with the remaining 90 percent having orgins and/or destinations within Lafayette. Considering that the Thruway is the most direct and straightest connection between US 90 and both I-10 and I-49/US 167, that’s no surprise whatsoever.
There are other considerations why Teche Ridge is not the catchall solution some would argue, but that alone is a major justification for the Connector alignment.

For the record, shown above is the LCG’s predicted ADT for 2040 with the Connector built and running. Notice how the freeway not only attracts traffic from the surface Thruway, but also sucks up traffic from other major arterials….and, being six lanes, it can easily handle the work.
In fact, building the Connector freeway as proposed along with converting the existing Evangeline Thruway into an “urban boulevard” would be far more ideal for both balanced economic development for the abutting neighborhoods AND moving current traffic. Indeed, the proposals put out by the Evangeline Corridor Initiative integrate the idea of a boulevard into all of their Connector freeway proposals, with the idea of one enhancing the other.
4) The Second Big Lie Of “Build Around”: A Bypass Isn’t Inexpensive, But It’s Certainly Cheap

This is another assertion that opponents of the Connector freeway have blurted: that a bypass would be so much less expensive than the “Con” through Lafayette. Over at Michael Waldon’s Connector Comments website in opposition to the project, there are frequent references to the BILLION AND A HALF DOLLARS that would have to go through the alleged Connector rathole, only to have to tear it down 20 years later for a righteous boulevard and bypass. In comparison, they frequently quote the Teche Ridge Bypass as the “common sense” route, because it would cost “half as much” and be built “twice as quick” because it avoids tender and suggestive areas.
Reality, however, does not support that analysis.
The most recent cost estimates for the proposed Connector freeway concepts for the core downtown area were released to the public, and they are quite revealing. Again, these cover the costs for only the central core area between Pinhook Road and the L&D rail spur crossing.

What jumps out at you is the serious sticker shock of the cost for the Cut-and-Cover option, due to both the major need of ROW displacements, the construction of the tunnel, and the high maintenance and operational costs for the tunneled section. What also should jump at you is that the Elevated option (especially Concept 4-2 with the Evangeline Thruway boulevard sub-option) actually cost less than the originally approved 2003 EIS/ROD alternative. $426 million is a long way from $1 billion, I’d think.
Now, let’s do some addition: the segment south of Pinhook Road includes an improved crossing of the Vermilion River, the University/Surrey interchange (pending what happens with the proposed runway displacement at Lafayette Regional Airport), and the three-level interchange with Kaliste Saloom Road. Using current values, that would probably add around $125 to $150 million to the cost. Then, you have the section from the L&D RR spur to near I-10, that would include the elevated interchange with Willow Street and improvements to the frontage road system from Donlon Avenue/Walmart Drive to Chalmette Drive, and possibly even the proposed Willow Street Circle/Gateway Arch. That would be another, say, $50 million. CSS design modifications and improvements required for mitigation would add probably another $20 million; then maybe $3 million for cleaning up the old SP railyard facility. Add all that up, and it comes to around $650 million to $700 million total.
Now, that doesn’t include the local tax commitment to local neighborhood projects that would be proposed by the ETRT/ECI/TIGER team, but that would be a local issue. With the Feds pitching 90% of the funding since this is a federal highway project involving a High Priority Corridor, the state match required would come to about $70 million.
Compare that to what the bypass proposals would cost. The LRX certainly would be less expensive due to it going around the city, right? Ahh, WRONG. The LRX would be a 60 mile long bypass extending along the perimeter of western and southern Lafayette Parish, extending even into northern Vermilion and Iberia Parish. The most recent estimates of the most preferred alignment for the LRX placed the total costs at around $1.2 BILLION dollars for a full LRX semi-loop connection from US 90 to I-49. Last time I checked, $1.2 billion was greater than $700 million. By a lot. Plus, LRX is being proposed as a tollway, funded by bonds which would be paid back through implementation of tolls throughout the facility. The Connector would be built totally “free”, perhaps with “private-public partnership” (P3) funds to ease the tax hurt, along with the rest of the I-49 South upgrade to New Orleans. (There was some early talk about tolling the upgrade of US 90, but a study showed that tolls wouldn’t even pay half of the total costs of the upgrade.)
That would leave the Teche Ridge Bypass, which is the preferred choice of darn near every single one of the Connector opponents. That is far more reasonable…but still, the truth reveals some flaws.
Teche Ridge proponents have usually quoted a 1994 “feasibility study” that was undertaken by officials in St. Martin Parish (funded by profits from casinos operating in that parish) for their belief in that alignment as a suitable alternative to the Connector. That study placed the approximate costs of that alternative at roughly $400 million for a complete bypass connecting US 90 south to I-49 north. That figure was also quoted in the affadavit filed by the Concerned Citizens of Lafayette group’s lawsuit against the FHWA and LADOTD to block the original 2003 FEIS/ROD. That affadavit was also submitted to LADOTD as an official comment to the 2003 Final EIS.
LADOTD’s response to the portion promoting Teche Ridge’s apparent cost benefit is below:

That’s $601M, not including ROW and engineering, in 2002 US$. Extrapolate for inflation and add the necessary costs, and you’re probably closer now to $700-750 million….which is nearly the same cost as what the extended and extrapolated costs of the Elevated Option concepts for the Connector freeway would cost in full.
And that’s not all, either….because Teche Ridge is not considered to be a suitable alternative for I-49 South, as is every other bypass alternative, it would require an entirely new process for feasibility and environmental study from the beginning. That’s two years for feasibility, two years for environmental and engineering, then securing funding, then getting it into the transportation program. The currently approved transportation programs by LADOTD and the Acadiana Regional Planning Commision (the official Metropolitan Planning Organization for Lafayette and the parishes surrounding Lafayette) are keyed on I-49 South using the Connector freeway and an upgraded US 90; so is the enabling federal highway legislation. To upset that by shifting I-49 South to Teche Ridge or the LRX would be at best time and money consuming; and at worst threaten to kill the entire I-49 South upgrade.
And, to make things even more problematic, there are signs that Teche Ridge isn’t even ecologically and environmentally as safe a bet as its proponents would argue. That proposal would basically traverse the thin ridge of high land that separates the Cypress Swamp/Lake Martin lowland swamp wetlands from Bayou Teche. Most of that land is now converted to farmland or remain as support for the surrounding wetland. That would pose a significant risk to such fragile and sensitive land use in the form of drainage from the freeway invading the fragile wetlands or pouring into Bayou Teche, which is a designated Scenic Waterway. The increased noise level of Teche Ridge could also disturb the flight path of endangered birds that use Cypress Swamp as relief for their annual fall/spring migrations. This would certainly raise the ire of federal and state wildlife officials. Other than the probable encroachment of the Chicot Aquifer and the possible need for some wetland acquisition for the LFT runway displacement, the Connector has really no major environmental or ecological issues otherwise.
5) The Biggest Lie of All

The final riposte of Mr. Sullivan’s letter promotes a nice vivid fantasy that if Teche Ridge….ahhh, I mean, if a freeway loop is built and highway traffic is forced to abandon the Evangeline Thruway, the latter can be reworked into a beautiful Complete Streets boulevard that will support everyone from walkers to bicyclists, and revive Lafayette like nothing other.
Funny, but that’s exactly what the Evangeline Corridor Initiative is attempting to do with the Thruway right now….with the Connector freeway in place. That theory actually works because, unlike Teche Ridge, the Connector actually will take enough traffic off the Thruway that it can be reworked to be neighborhood friendly. And, surprise…it does it without even traversing Sterling Grove or McComb-Veazey or even Freetown-Port Rico, while allowing full access and connectivity underneath the freeway structure. By contrast, unless you are planning on downgrading the entirity of US 90 back down to 2×2 and dismantling the proposed interchanges now planned or under construction, you simply are not going to remove much traffic from the Thruway even with Teche Ridge built. If you think the Thruway is a disaster now with no sidewalks or consideration for the neighborhoods with 64K VDT, imagine it reduced to 4 lanes with 90K VDT. Even the best “boulevard” will fail that test.
As for hurricane evacuation effectiveness: only Connector opponents like Mr. Sullivan can explain how diverting hurricane evac traffic to the east through a 4-lane bypass and a reduced 4-lane boulevard would be better than a direct access 6-lane elevated freeway with full shoulders which would also allow for contraflow and also include the surface-level Thruway/boulevard as a backup. Not to mention that Teche Ridge would do absolutely nothing for an evacuation of Broussard or Youngsville, nor for evacuees escaping from Vermilion Parish using US 167 north through Lafayette.
Oh, and the example that Mr. Sullivan gives for his ideal Evangeline Thruway? That’s taken from a YouTube video dated January of 2016 that was linked in his letter showing a plan for removing a portion of the I-70 corridor in Denver. There’s one small problem: that’s not the finally approved plan for that corridor. The removal (and diverting I-70 to I-270 and I-76) was considered and then rejected as too expensive and disruptive; the ultimate final solution was to bury the existing I-70 corridor under a capped tunnel and build a boulevard section above it. You know…like the ECI’s Depressed/Capped Mainline and DOTD’s Cut-and-Cover Concept 6-2.
Finally, let me conclude with this: Yes, driving interstates and highways through local poor communities in the 60’s without any consideration for the neighborhoods affected was a huge, huge error in judgement, and in some cases, a deliberate crime. However, those crimes are history, and those highways are there, serving their stated purposes of moving people and goods to where they are wanted and needed. While it is fair and appropriate to question today whether those highways can be reformed or removed, those questions should be resolved on an individual case-by-case basis, with everyone’s input and feedback involved. And, whatever alternatives are proposed must meet the desires and needs of all who use the roads, not just some planner’s wet dreams for “redevelopment” or some people’s desire for bringing back “the past”. Whether we like them or not, however ugly they may be, freeways still move people who want their cars and trucks and vehicles; maybe instead of merely tearing them down or opposing them at all costs, we might attempt to build them with everyone’s needs balanced out.
The I-49 Lafayette Connector project is the most recent test as to balancing traffic need with the desire for abutting neighborhood improvement. The most recent plans offered meet those goals of balance. It would be a shame if NIMBYism and obstructionism for the mere sake of obstruction would kill the best chance for Lafayette to both relieve their most serious traffic issue AND lay the seeds for revival of its downtown and central core. A loop will be warranted down the line, even including Teche Ridge….but the Connector is needed TODAY. Let’s work together to build it to the best way possible, and save the bypass for later.